


2021 IPPE: effects of mushroom stumps on amino acid digestibility
Consumer eat tons of of Agaricus mushrooms leaving large stump waste - this waste can be used by poultry producers in their broiler rations.Part of Series:
< Previous Article in Series
During the 2021 International Poultry Scientific Forum, Pennsylvania State University’s Logan Erb presented his team’s research on the effect of mushroom stump waste inclusions on broiler amino acid digestibility over a 21-day period.

Research design
For the feed, mushroom stumps were dried at 65.6 degrees Celsius for 120 hours and mechanically shaken to remove dirt and peat moss. Particle size was then reduced using a hammer mill. For the broilers, the study used 12, 20-week-old intact Single Comb White Leghorn roosters, fasted for 24 hours in advance of the experiment.
After creating a nutrient profile for the mushroom stump waste, four isochloric and isonitrogenous treatments, all varying in mushroom stump waste inclusion, were created:
- 0% mushroom stump waste
- 1% mushroom stump waste
- 3% mushroom stump waste
- 5% mushroom stump waste
These diets all met the nutrient requirements of Cobb by Cobb straight-run broilers from Day 1 to 21 of age.
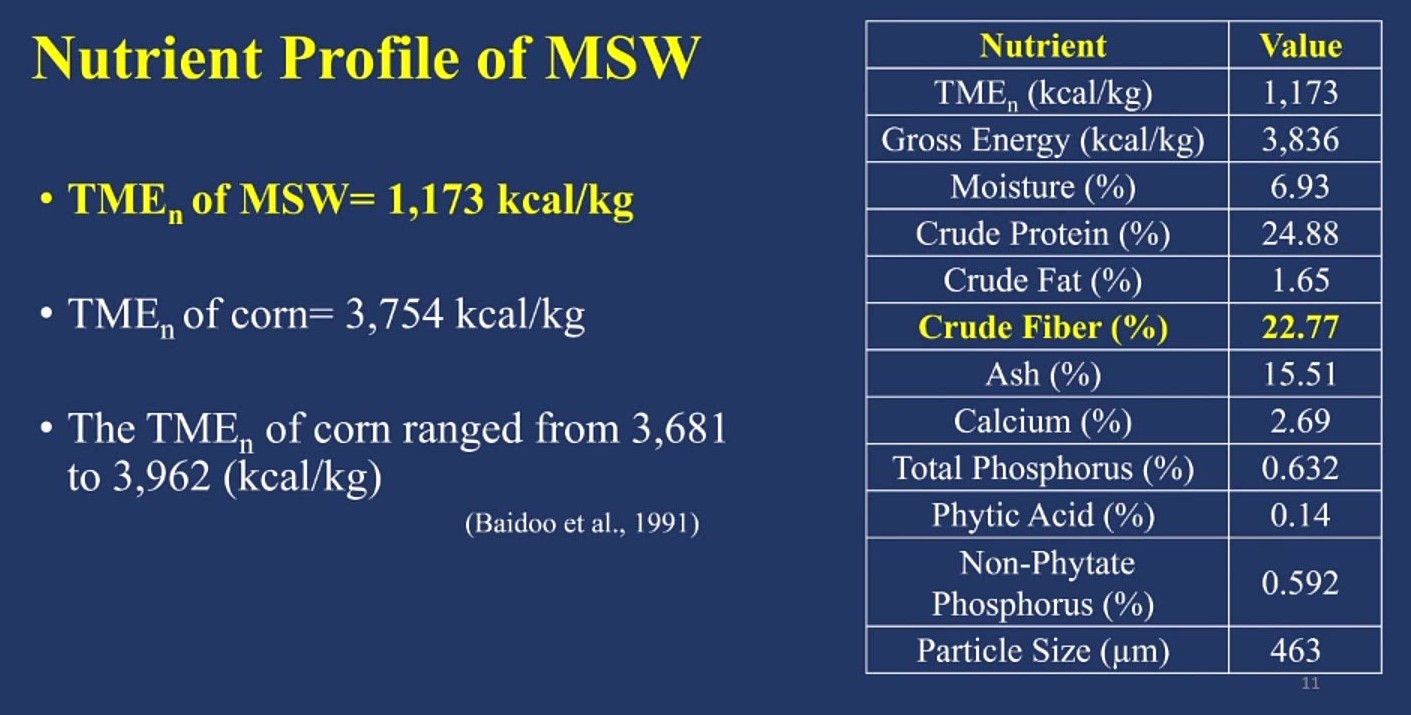
Once the crop was fed, the researchers collected, weighted and dried excreta 24 hours post-feeding. It was then analyzed for crude protein and gross energy to give the true metabolizable energy value of mushroom stump waste.
Bird performance measurements were taken from Day 1 to 21. The birds were weighed twice, on Day 1 and on Day 21. Feed intake was recorded on Day 21. Additionally, on Day 18, titanium dioxide was included in the diet at 0.2%. This was used as an indigestible marker required to calculate apparent ileal amino acid digestibility (AIAAD).
At the end of the 21 days, the birds were handled and weighed, feed weights were recorded and select birds were euthanized. From those birds, the distal ilea was extracted, and the contents were gently flushed out using a 20 milliliter syringe and distilled water. The pooled digesta was then freeze dried and analyzed for amino acid and titanium concentration, then calculated to give the apparent ileal amino acid digestibility.
Research findings
According to Erb, neither feed intake per bid, nor mortality, were affected by mushroom stump waste inclusion. Average bird weight differences were non-significant.
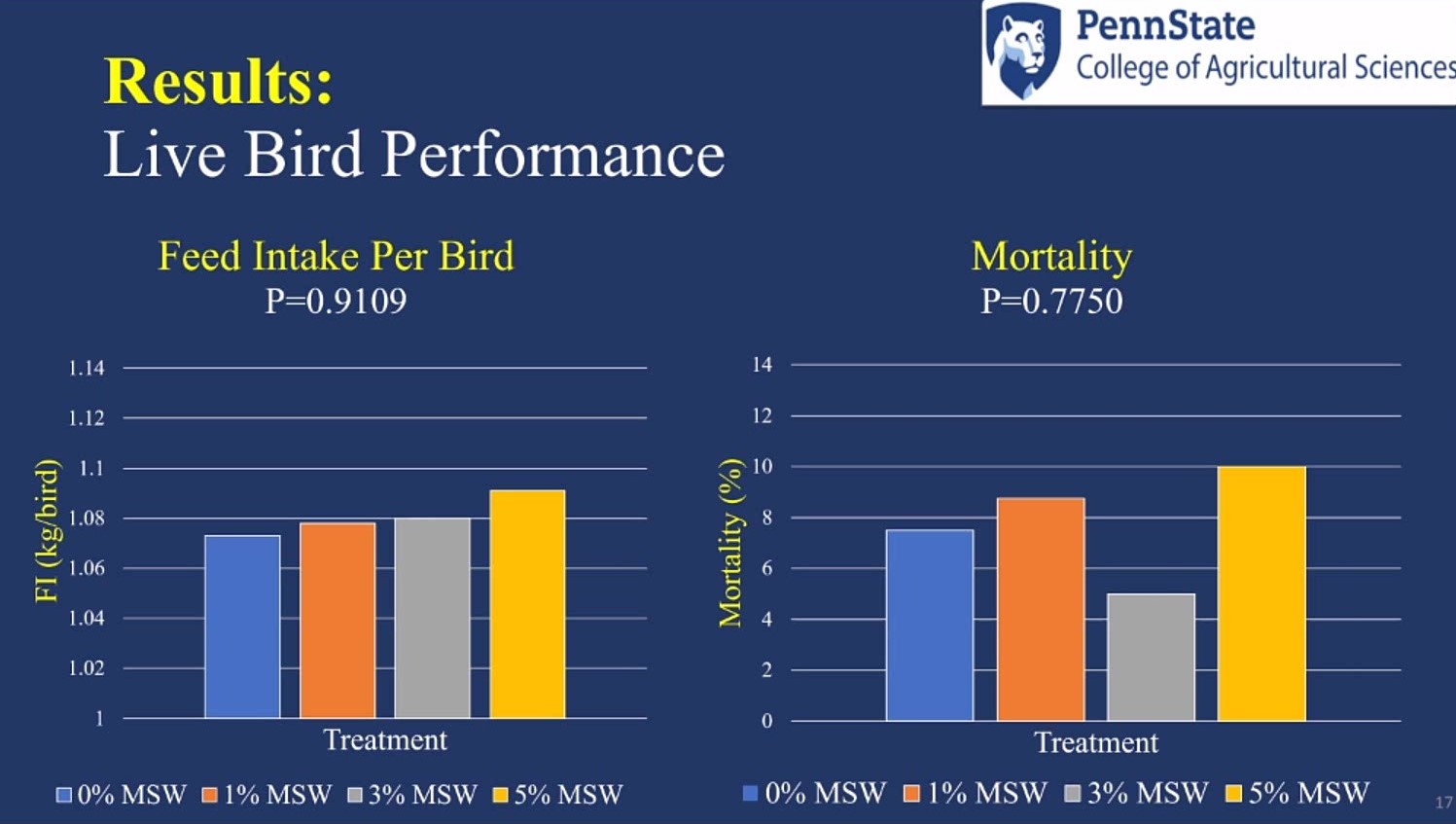
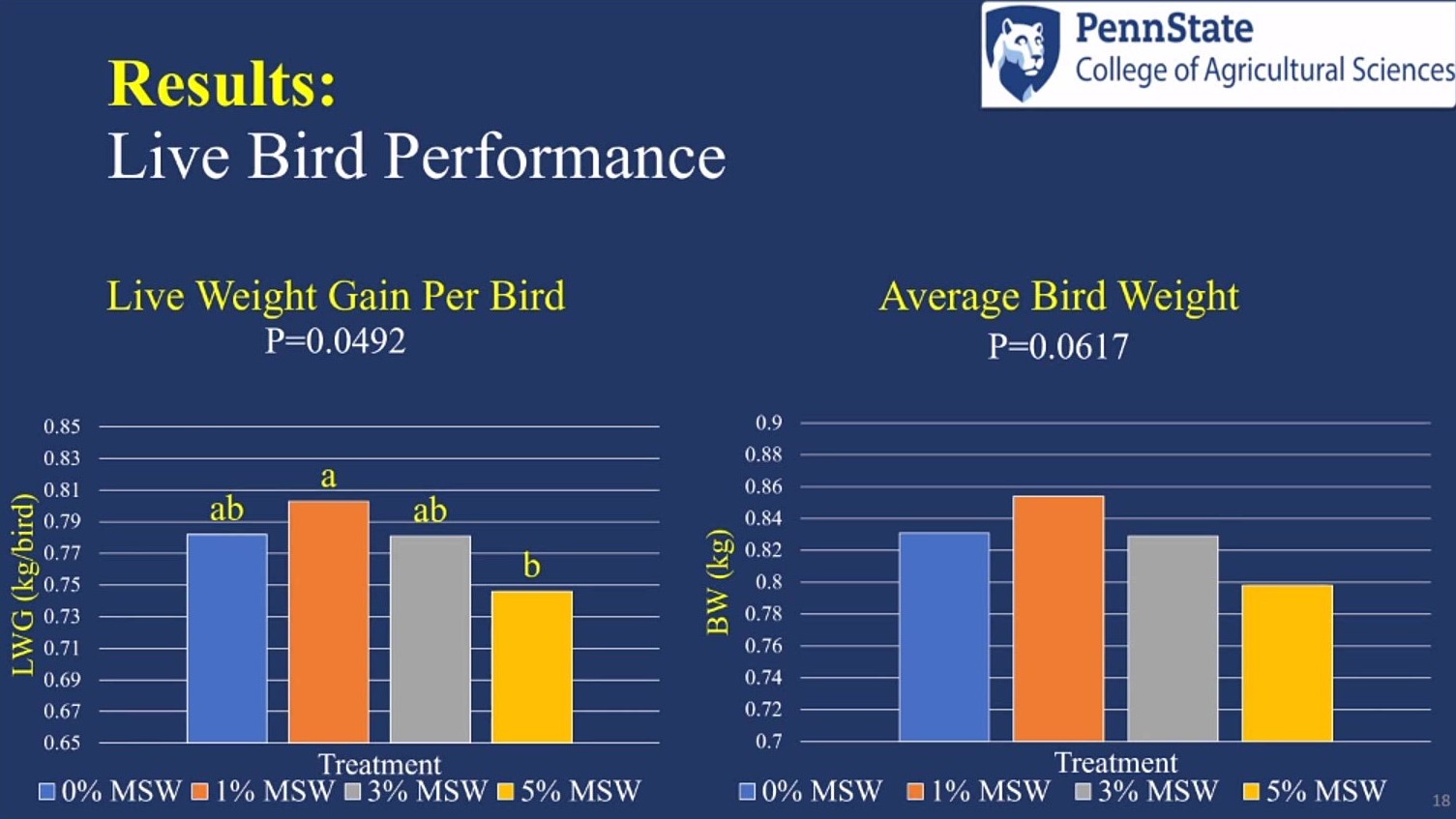
However, the 1% mushroom stump waste treatment showed high live weight gain, the 5% treatment showed low live weight gain, and the 0% and 3% treatments were intermediate.
There were also significant differences in feed conversion ratio (FCR). The 5% treatment had the highest FCR, while the 0%, 1%, and 3% treatments had lower FCR. There was a 10.5 FCR difference between the 5% and 1% treatments.poultry/Events/IPPE/Research/ippe-mushroomstump-results2.jpg
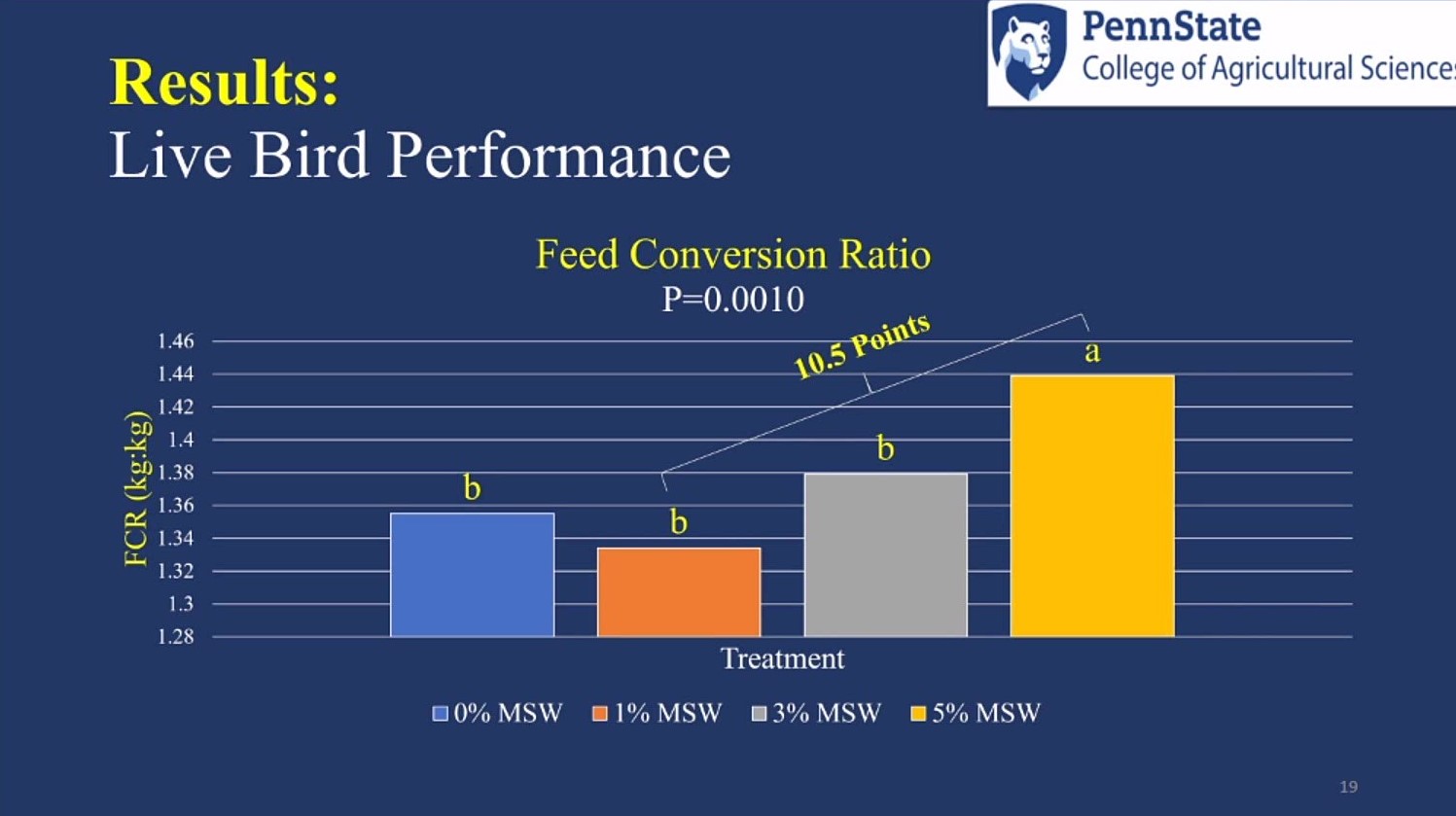
Overall, this study demonstrated that inclusion of mushroom stump waste products in up to 3% of treatments show no reduction in broiler performance. However, amounts of 5% or higher would reduce performance. Additionally, AIAAD did not differ for any of the 19 amino acids analyzed.















