



Aviagen Group: Decades of Breeding for Welfare & Sustainability: Welfare Traits & the Environment
Learn more about Aviagen Group's sustainability traits & environmental sustainabilityPart of Series:
< Previous Article in Series Next Article in Series >
Editor's note: This article is an excerpt from the Aviagen Group's Decades of Breeding for Welfare & Sustainability Report and additional articles will follow. The Report is designed to demonstrate Aviagen's commitment to genetic improvement of welfare and sustainability of broiler and turkey breeds. Plus, it covers much more like techniques to ensure robustness and new methods to improve selection and genetic progress. To read or download the complete report, click here.
Welfare and Sustainability Traits
Aviagen has a long history of incorporating welfare and sustainability measurements into its breeding program to drive progress (Figure 4).
The expansion to include turkey breeding programs has allowed sharing of resources and exchange of new ideas and techniques between the breeding programs.

Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability has long been a core focus for Aviagen. Whilst increasing flock outputs through improvements in traits associated with weight, livability, egg and meat yield play a key role in this, the amount of feed a bird requires to develop and grow is key to the global footprint of poultry production. FCR is the single most important trait for reducing the environmental impact of poultry production (Jones, 2008).
The improvement seen in FCR within both broilers and turkeys has greatly reduced the carbon footprint of poultry meat and also reduced the amount of environmental pollutants associated with poultry production.
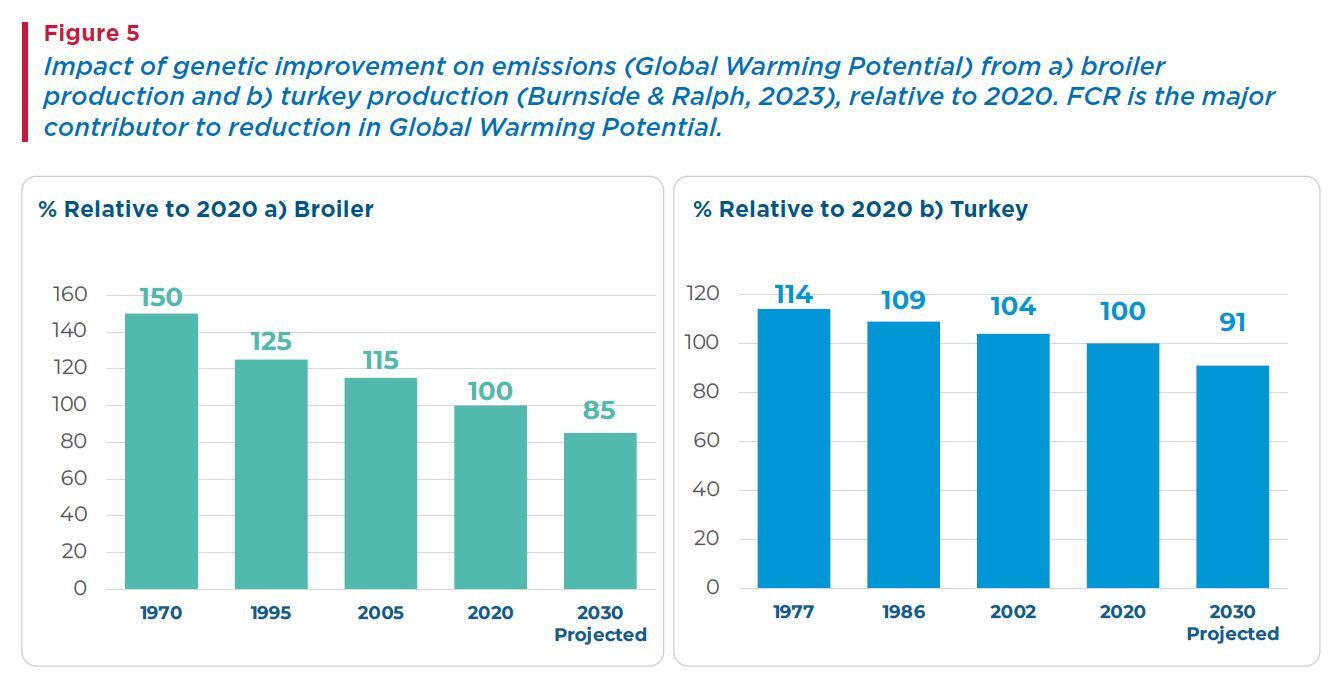
Figure 5a shows Aviagen calculations of the relative environmental impact of broiler production over time. Broiler genetics from 1972 had a 50% higher environmental impact than 2020 genetics and future genetics will have 10% lower carbon footprint by 2030 than the bird today, which is in line with the estimations made by Jones (2008).
Turkey genetics resulted in a 20% lower carbon footprint between 1977 and 2020, with an expected 10% improvement by 2030 because of improvements made in the breeding program (Figure 5b). These improvements of about 1% per year are primarily driven by genetic improvement of FCR.
For decades, intensive selection for improved FCR has resulted in a highly feed efficient animal that is far more sustainable than many alternative meat sources.
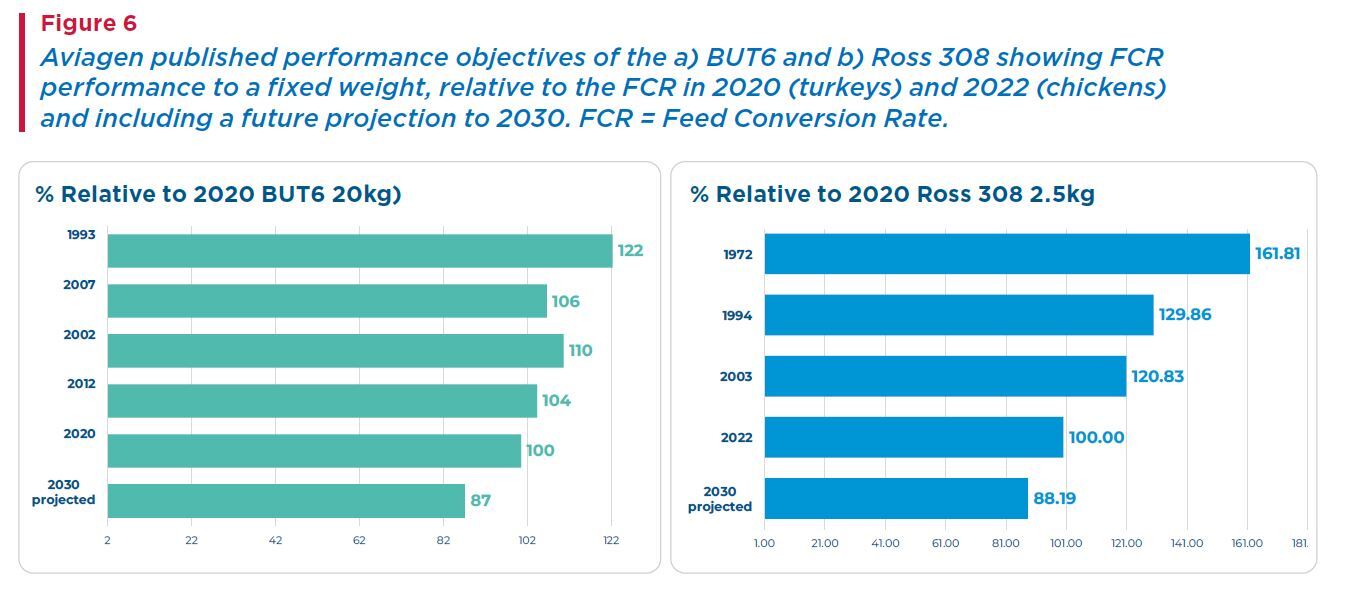
This can be seen in the evolution of the performance objectives published for the BUT6 and Ross® 308 (Figure 6).
Historically FCR was assessed by measuring feed consumption and weight of birds in individual pens. Since 2004 in broilers and 2006 in turkeys, Aviagen has pioneered the use of feed stations, which record individual bird feed intake using transponder identification within a group environment (Figure 7).

This allows the selection of birds with genes associated with improved feed efficiency while the birds are free to express natural behavior. The feed station technology has been highly successful and example of its importance can be seen in the 50% increase in testing capacity in the turkey breeding programs since 2018.
The feeding stations have also allowed the study of feeding behavior, which has shown that broilers and turkeys share the same structure of short-term feeding behavior, which is regulated by levels of satiety. This was also observed when comparing broilers, turkeys and ducks to cattle, pigs, dolphins and rats (Howie et al., 2010, Tolkamp et al., 2011). The correlations between feeding and drinking behavior traits with performance traits is low. There is a wide range of feed and drinking behavior strategies in the broiler and turkey populations, which is important for their adaptability to a wide range of environments and production systems. Individual bird FCR alongside livability, robustness and weight have jointly contributed to the significant improvements seen in flock FCR.
Since 2014 in broiler and 2017 in turkeys, Aviagen has been applying genomic selection in its breeding programs. Genomic selection increases selection accuracy which results in greater rates of progress across traits. This has been particularly beneficial for FCR where it is not possible to measure the FCR of every individual and the selection accuracy of unmeasured birds is markedly improved thereby enhancing progress in the environmental sustainability of poultry production.

To read or download the complete report, click here.













