



Evaluation of an IBD immune complex vaccine administered in ovo compared to an intermediate plus drinking water vaccine on a Belgian farm
Prevention of Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) through vaccination can be achieved by different types of vaccines available on the market and by several routes of administration.Gumboro live attenuated vaccines contain live viruses that replicate and colonize the bursa of Fabricius, generating protection to the birds mainly by competitive exclusion and the generation of antibodies. Since the maternally- derived antibodies (MDA) can interfere with the vaccine virus strain replication, the optimal day of vaccination has to be calculated in conventional live attenuated vaccines applied through drinking water, in order to avoid this neutralization. Moreover, chicks from different breeder flocks can show different immunity levels, which is the reason why it is common to administer two doses of the vaccine at farm level.
To avoid the maternal antibody neutralization problem, there are so-called technological vaccines on the market such as immune complex vaccines. Immune complex vaccines are based on the combination of a live attenuated vaccine strain coated with specific antibodies against the Gumboro virus (IgY), which permits administration at hatchery level whilst being capable of providing protection even in the presence of maternal antibodies in the chicks. Thanks to this, the onset of immunity is adapted to the protection needs of each chick, avoiding the feared gap in immunity.
GUMBOHATCH® is a new immune complex vaccine against Infectious bursal disease (IBD) developed by HIPRA. This vaccine has introduced a different formulation (IgY of egg origin) and control parameters to guarantee the complete coating of the virus at the time of inoculation. All these new improvements ensure the maintenance of the maximum potency of the vaccine and consistent results in the field, whilst avoiding the risk of immunosuppression.
In this article, two type of vaccines administered via different routes are compared: an immune complex vaccine administered in ovo at the hatchery and an intermediate plus live attenuated vaccine applied through drinking water at the farm.
Field trial procedure and results
The present field trial was performed to compare the efficacy and safety of GUMBOHATCH® with a reference intermediate plus drinking water vaccine. It was conducted on a Belgian commercial broiler farm with two identical houses:
Vaccine |
Route of administration |
Number of birds |
Days of age |
GUMBOHATCH® |
In ovo (hatchery level) |
53,099 |
18 days of incubation |
Commercial intermediate plus |
Drinking water (farm level) |
53,213 |
Based on IBDV titres of day-old chicks |
After vaccination, different parameters were evaluated:
Evaluation |
0 days |
21 days |
28 days |
35 days |
RT-PCR (wild and vaccine strains) |
X |
X |
||
IBD antibody titres (BIOCHEK® IBD ELISA) |
X |
X |
X |
|
Macroscopic bursal lesions and bursa to body weight ratio |
X |
X |
X |
Since both vaccines evaluated were live vaccines, it was expected that vaccine virus would be observed in the animals’ bursa of Fabricius after performing RT-PCR. Very virulent IBD virus was detected only in birds vaccinated with the reference drinking water vaccine, whilst the group vaccinated with GUMBOHATCH® always showed the vaccine strain. GUMBOHATCH® showed better protection by competitive exclusion on all the test days.
Regarding the serological results, GUMBOHATCH® showed significantly higher ELISA titres, without the need to calculate the best day for vaccination.
Finally, macroscopic bursal lesions and bursa to body weight ratio were compared:
- The prevalence of macroscopic lesions was the highest at 21 and 28 days of age in the GUMBOHATCH® and reference vaccine group, respectively, indicating different times of initial replication for the vaccines.
- The bursa to body weight ratio was similar for both groups: mild petechiae inside the bursa were observed in 12.5% in both groups and two bursas of the reference vaccine group showed an abnormal consistency.
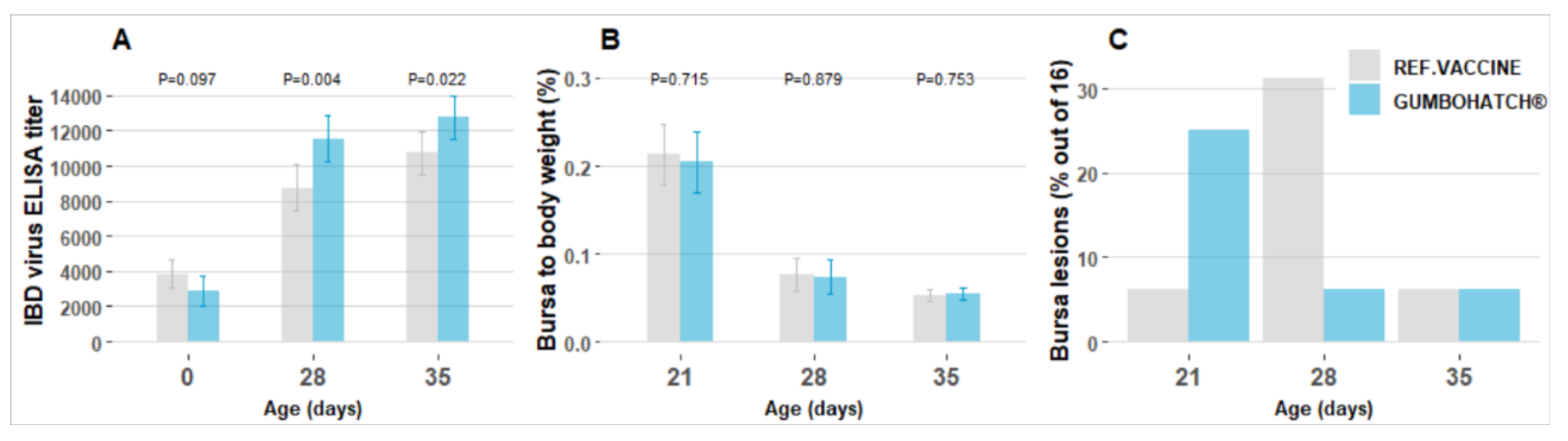
On the farm studied, GUMBOHATCH® showed superior protection compared to an intermediate plus drinking water vaccine, as demonstrated by higher titres to the IBD virus and the absence of wild strains. Safety parameters were similar. |
Conclusions
Gumboro live vaccines allow the vaccine viruses to reach the bursa of Fabricius and achieve the prized immunity by competitive exclusion. For optimal results, the vaccine virus should arrive at the right time for each chick, which it is not always possible to achieve with simple live vaccines. This trial reinforces the advantages of GUMBOHATCH®, a next-generation immune-complex IBD vaccine for hatchery application, compared to a reference live vaccine administered in drinking water.









