


Monimax® – Efficacy and Performance
Monimax® is a new product that combines the strengths of the synthetic compound nicarbazin with the ionophore monensin, resulting in a unique new product for coccidiosis control.- Monensin interacts with the parasite during the motile stage (sporozoites and merozoites) and does not penetrate the intestinal cells.
- Nicarbazin interacts later during the lifecycle of the parasite and can penetrate the intestinal cells (1st and 2nd generation schizonts).
The different mode of action of monensin and nicarbazin results in an optimal efficacy. There is a synergistic effect between nicarbazin and monensin, resulting in a high performing product.
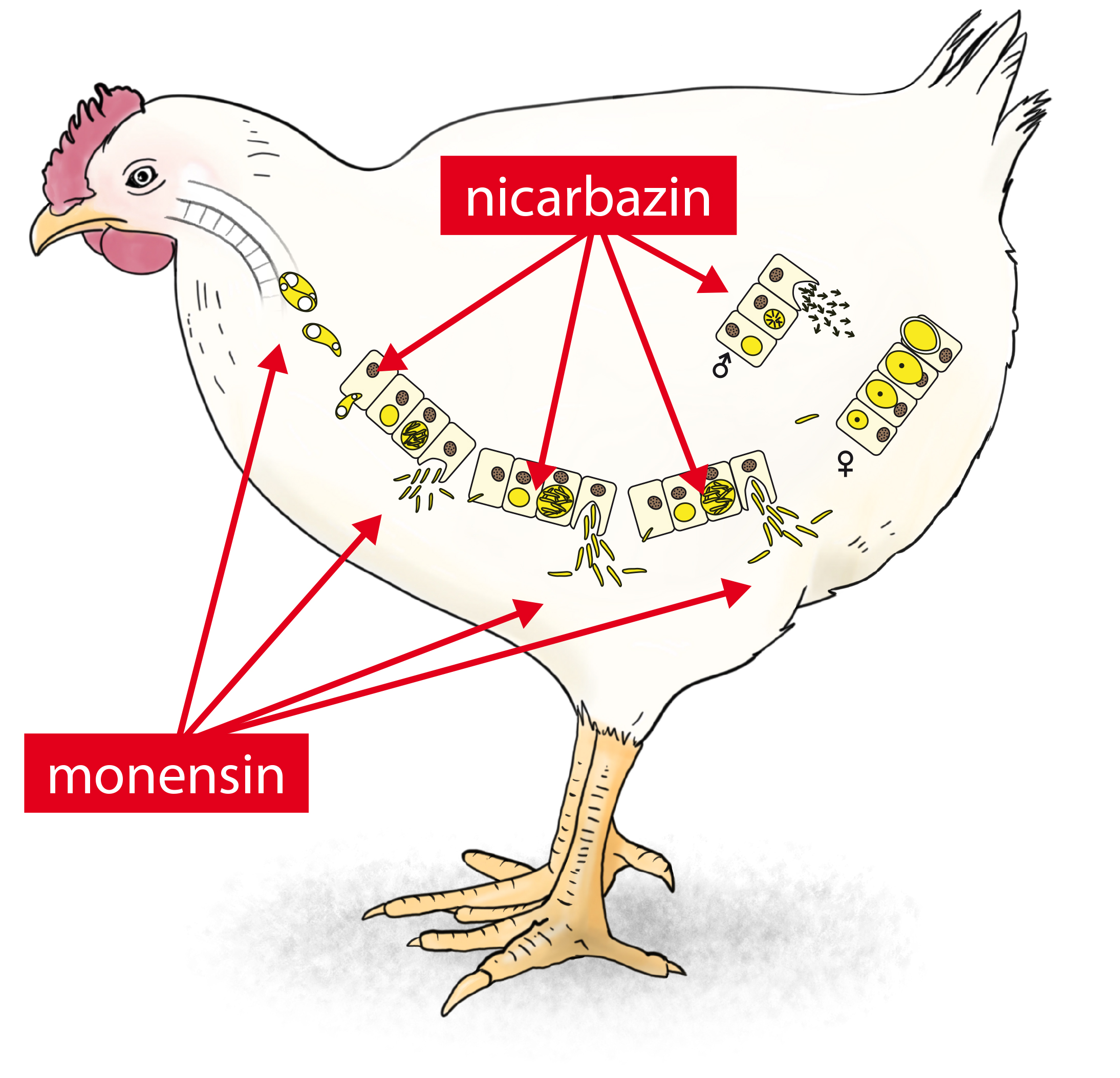
Synergy of 2 strong active compounds
An anticoccidial sensitivity trial (AST) has demonstrated this synergistic effect between nicarbazin and monensin: the combination of both products performed better than the products individually. Monensin at 40 ppm did not reduce lesions for any of the Eimeria species. Nicarbazin at 40 ppm significantly reduced the lesions for E. tenella but the other Eimeria species were not significantly affected. The combination of nicarbazin and monensin (both at 40 ppm) significantly reduced the lesions for all Eimeria species.
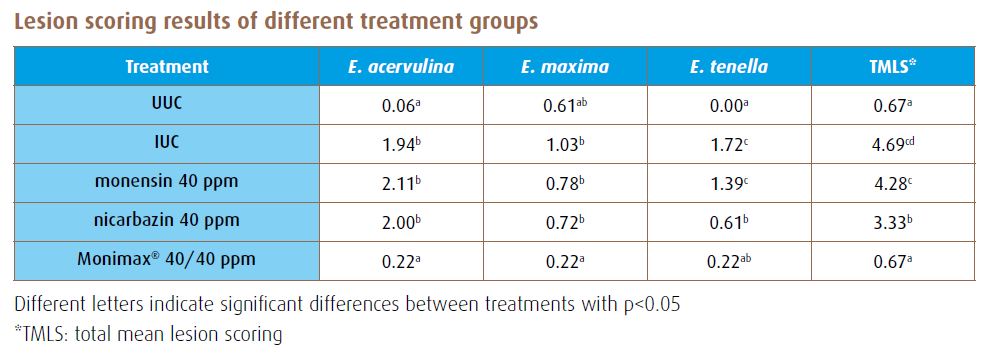
These results are proof of the synergistic effect between monensin and nicarbazin.
Although Monimax® is a new product, the active compounds have been on the market for many years, so development of resistance is a legitimate concern.
Recent feedback from the field indeed suggests reduced efficacy of the often used nicarbazin/narasin combination product, currently on the market.
For this reason, a meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the effectiveness of Monimax® against recent Eimeria field strains in comparison to nicarbazin/narasin.
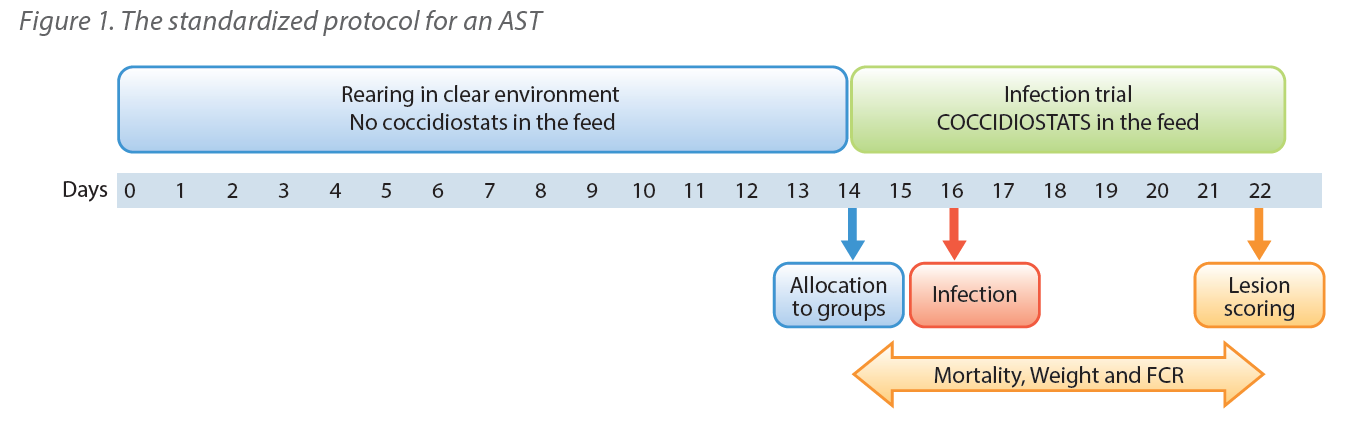
The meta-analysis was performed using the data of 27 different anticoccidial sensitivity tests (ASTs) conducted over a 7-year period (2013-2019). The Eimeria isolates were collected from commercial farms from 13 different countries with different anticoccidial control programs.
The sensitivity trials were conducted in 2 different research institutes, using a comparable, standardized AST protocol (Figure 1). In short, groups of birds, reared in cages, are supplemented with Monimax® or nicarbazin/narasin starting 2 days before oral inoculation with different Eimeria field strains. About 6 days after inoculation, the severity of lesion scores (according to Johnson and Reid, 1970) and the performance is determined and compared to an uninfected, untreated control group (UUC) and an infected, untreated control group (IUC). All coccidiostats are used at the currently registered European dosages.
Average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADI) and feed conversion ratio (FCR) over a week’s time period were compared in a meta-analysis from 27 standardized sensitivity trials. In feed application of Monimax® was compared to both control groups and to the inclusion of nicarbazin/narasin combination.
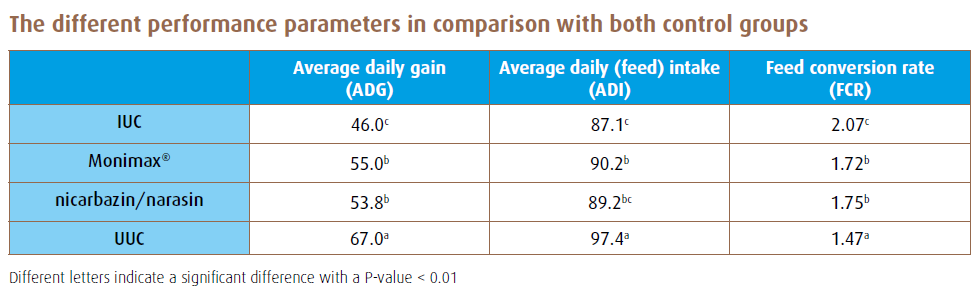
Monimax® resulted in significantly higher values for all measured parameters (ADG, ADI and FCR) compared to the IUC. Although the difference is not statistically different, Monimax® resulted in better performance compared to the nicarbazin/narasin combination.
Lesion scores were determined according to the Johnson and Reid scoring system and the least square mean (LSM) per species is shown in the table below.
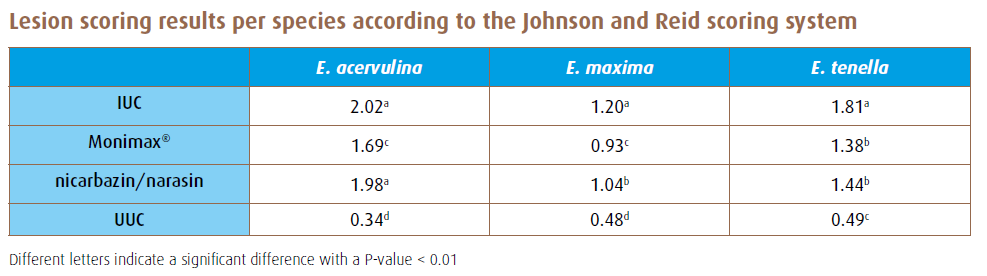
The combination of nicarbazin and narasin did not deliver a significant reduction of E. acervulina, whereas Monimax® resulted in a significant reduction for all species (E. acervulina, E. maxima and E. tenella) compared to the IUC. Monimax® resulted in significantly lower lesions both for E. acervulina and E. maxima compared to nicarbazin/narasin.
Control of Eimeria acervulina, is very important as prevalence data (collected from Aviapp®) demonstrate that Eimeria acervulina is the most frequently diagnosed Eimeria when monitoring broilers in Europe, followed by Eimeria maxima and Eimeria tenella. When plotting out lesion scoring data by the age of the birds, from more than 4000 flocks over the last 3 years, Eimeria acervulina is the main driver of the total mean lesion score.
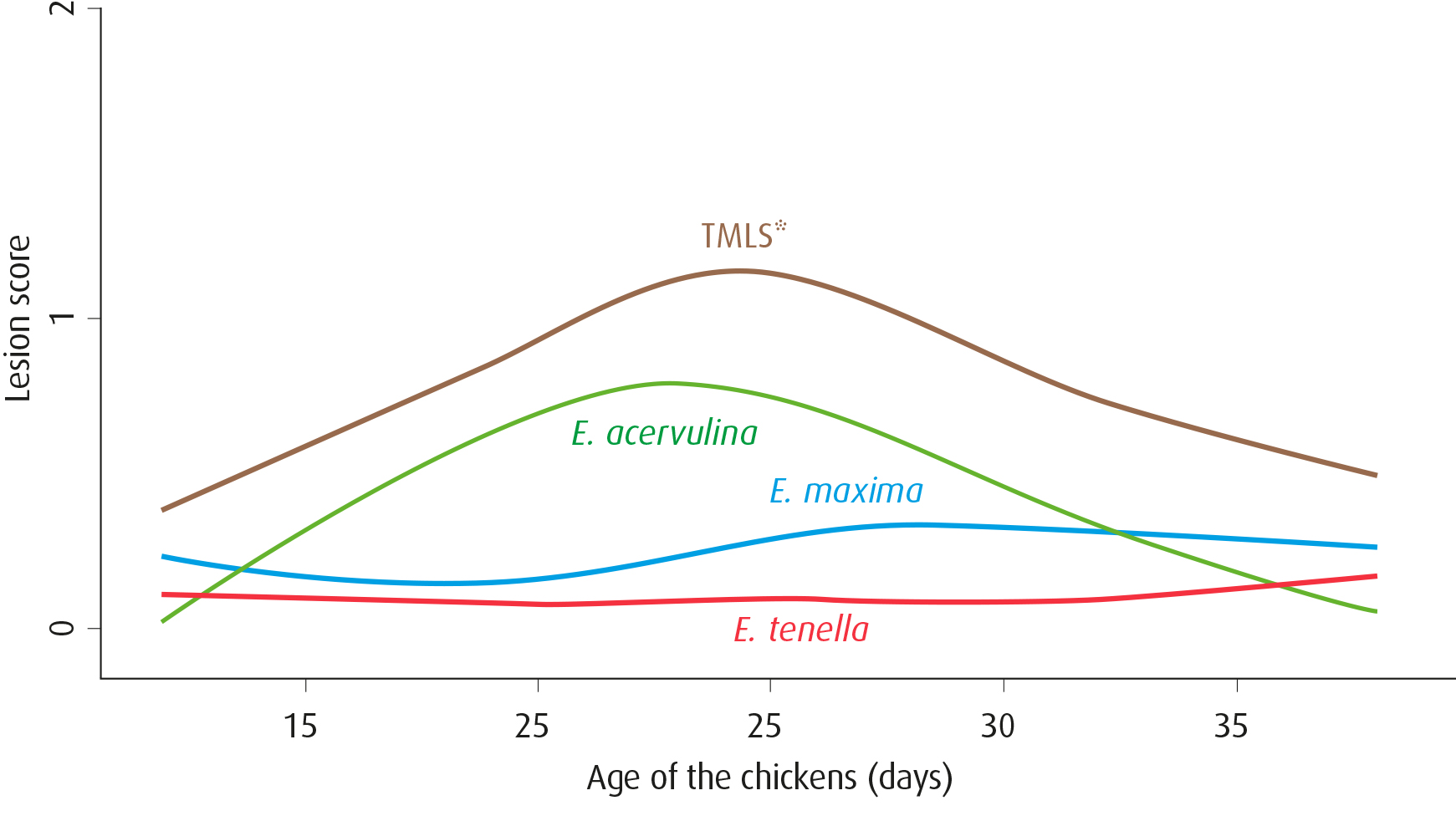
Total mean lesion score (brown) and average lesion scores of Eimeria acervulina (green), Eimeria maxima (blue) and Eimeria tenella (red) per age. The graph comprises data from 4,692 European flocks scored between 2016-2019.
Conclusion
Monimax® is a new anticoccidial on the European market. The combination of nicarbazin and monensin results in a product with proven efficacy because of the synergistic effect of the 2 compounds.
Monimax® has proven to significantly increase zootechnical and parasitological parameters in an extensive study including data of 27 standardized sensitivity trials.
Results were improved in comparison to birds receiving the nicarbazin/narasin combination due to the significantly better control of Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria maxima. From a practical point of view, this is especially important as E. acervulina is the most prevalent Eimeria species in Europe.










