



rHVT-ND vaccine makes the difference vs. Inactivated ND vaccines in Newcastle disease control
As we are approaching 100 years since it was reported for the first time, Newcastle disease (ND) continues to challenge the poultry industry globally causing in some countries devastating losses. Over this time, improvements have been made for better disease control, but some limitations have been encountered. Recent advances in vaccine development have allowed a significant impact in the control of this disease. Novel ND vaccines permit massive and uniform vaccine administration at the hatchery to induce early and lifelong lasting immunity with minimal additional field interventions have been achieved.
Technological advances in the molecular biology field have allowed the design of a genetically engineered vaccine against ND to make it more effective than conventional vaccines with eliciting broader immunity with lifelong duration as well as avoiding interference with the maternally derived antibodies. Additionally, mass administration at the hatchery ensures uniform immunization without the limiting factor that the maternal immunity causes to inactivated conventional ND vaccines delaying and lowering their immune response without mentioning the tissue reaction, transmissibility of ND field virus challenges and risks involved in self-injection of the operators during vaccination. The cumulative advantages carried in the implementation of Vectormune® ND vaccination at the hatchery as part of a regular health program makes it the ultimate advanced tool for ND control.
Economical Advantage
Large scale field trials allow to measure differences and consistency in ND protection when vaccination programs are compared to determine the distinctive benefits of one ND vaccination program over the other and to translate them into economic advantages.
Table 1. Production performance parameters comparing ND vaccination programs
Production Parameters |
Inactivated ND |
Vectormune® ND |
P value* |
Number of flocks |
39 |
13 |
|
Chick quantity (m2) |
14.89 |
14.82 |
>0.05 |
Slaughter age (Days) |
41.39 |
41.71 |
>0.05 |
Slaughter weight (Kg)* |
2.50 |
2.60 |
<0.05 |
FCR* |
1.73 |
1.70 |
<0.05 |
Total mortality (%) |
5.33 |
4.88 |
>0.05 |
EPEF* |
332.03 |
348.36 |
<0.05 |
*Statistical significance when P values are < 0.05 |
|||
Here, we present an example of a comparative field performance study involving over one million birds, from the same commercial operation and similar management system, receiving 2 distinct ND vaccination programs and grown up to 41 days of age targeting 2.5 Kg average live body weight. Commercial broiler flocks were raised during a contemporary period of time. Production performance parameters are presented in Table 1 indicating the statistical significance for the main parameters measured with its consequent economic benefits (Table 1).
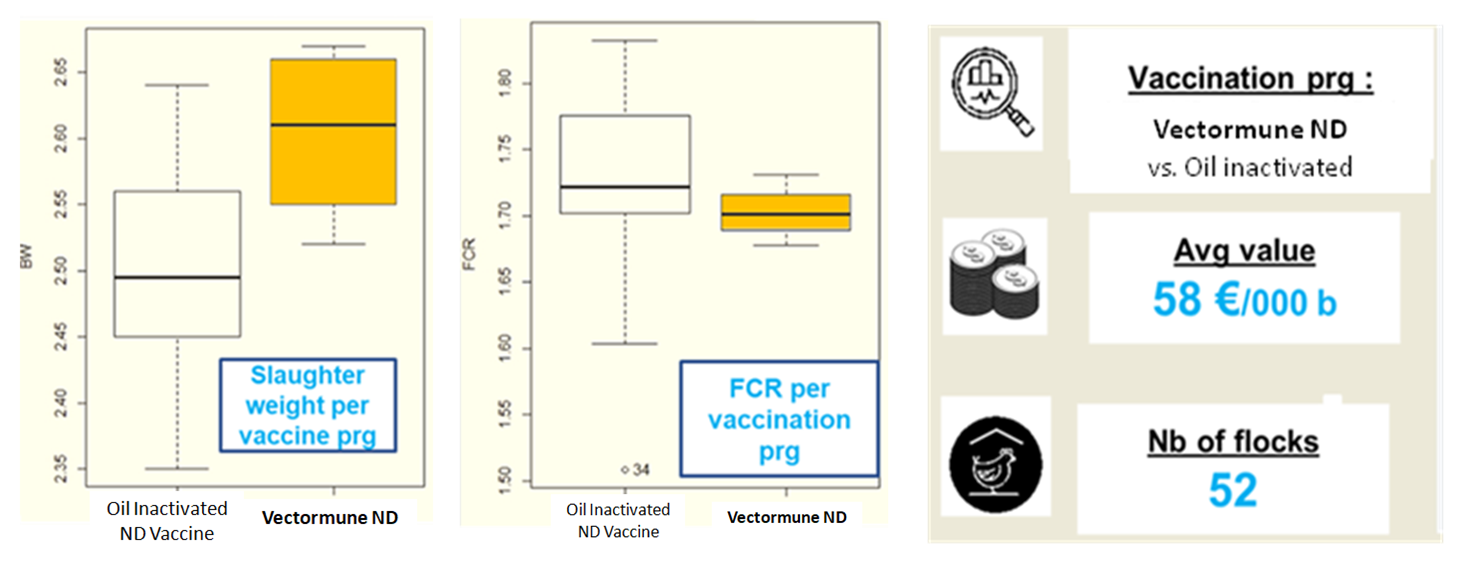
The economical benefits were calculated based on the production differences considering additional 100 g/ bird in body weight and 3 points lower in the feed conversion ratio with the Vectormune® ND vaccination program which translates into 58 Euros per 1,000 birds in this study.
The economical benefits generated with Vectormune® ND are the result of its 3 unique characteristics:
- Elicits all types of bird’s immunity
- Avoiding MDA interference
- Minimize ND field virus transmission
Protection Parameters against ND
Several parameters must be included in the evaluation of a ND vaccine to be considered protective against this viral disease. Effective ND vaccines permit individual and mass administration at the hatchery, either by In-Ovo or subcutaneous routes, to ensure an uniform and consistent immunization early in the life of a bird. Additionally, the immunogen must elicit cell-mediated and systemic and local antibody-mediated immunity inducing early and lifelong lasting immunity with minimal additional field interventions. Several factors are listed in Table 2 to be considered in the selection of a ND vaccine as part of the health program of a given flock, with minimal changes under different field pressure conditions.
Table 2. Factors to consider in broiler hatchery vaccination for ND control
|
Protection Parameters |
Vectored |
Inactivated (Oil emulsion) |
|
Massive immunization via SQ |
YES |
YES |
|
Massive immunization via In-Ovo |
YES |
NO |
|
Avoiding MDA Interference on Immunity |
YES |
NO (Delayed & Lowered response) |
|
Onset of Immunity with MDA* |
2-3 weeks |
4-6 weeks |
|
Avoiding tissue reaction |
YES |
NO |
|
Systemic Antibody-Mediated Immunity |
YES |
YES |
|
Cell-Mediated immunity |
YES |
NO |
|
Local immunity |
YES |
NO |
|
Vaccine safety |
YES |
Operator’s self-injection risk + local injury risk in chicks |
|
Virus excretion (Oral & Cloacal) after NDV field challenge (shedding control) |
Minimum ND virus transmission (very low ‘’r value’’) |
Much higher virus transmission |
|
Bird’s life sustained immunity |
YES |
NO |
|
Antigen matching to field prevalent NDV |
Not needed |
Needed for better immune response |
*MDA: Maternally-derived antibodies (Passive immunity).
1. Elicits all types of immunity
Numerous studies have demonstrated the activation of the different branches of the immune system after vaccination with Vectormune® ND. Evaluation of several types of immune responses (Cell-mediated, systemic and local antibody-mediated immune responses) under severe challenge studies using a variety of very virulent ND viruses that have emerged in different regions of the world, have demonstrated the broad spectrum of protection and lifelong immunity elicited by Vectormune® ND when compared with conventional inactivated vaccines.
2. Avoiding MDA Interference on Immunity
Achieving earlier protection against ND at the hatchery with a combined passive and active immunity offers immediate protection benefits and allows the build-up of a strong and lifelong immunity. This may be accomplished with an adequate immunization program. Vectormune® ND vaccine strain generates its early immunity through cell to cell replication without getting in contact the systemic maternal antibodies. The use of conventional live inactivated vaccines at the hatchery in the presence of maternally derived antibodies has been proven to be ineffective with a delayed and low immune response.
3. Minimize ND field virus transmission
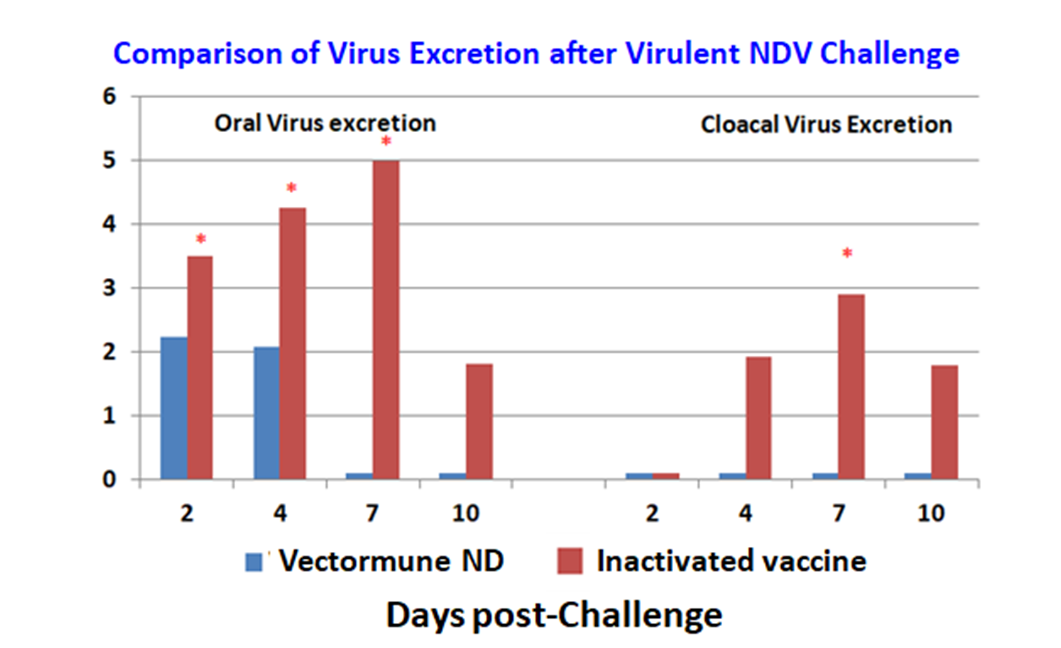
Vaccination against ND at the hatchery has significant advantages, especially when the most effective ND vaccines are included in the program. Virulent challenge studies help to evaluate and compare the protection given by different vaccination regimens. Morbidity, mortality and diverse types of immune responses (Cell-mediated, systemic and local antibody-mediated immune responses) were measured after very virulent ND challenge to evaluate the protection given by a conventional ND vaccination regimen versus a vectored vaccine administered to commercial broilers at the hatchery. Virulent ND challenge virus excretion helps to measure efficacy in the control of systemic virus replication after inoculation (Figure 1). Challenge with a vvNDV (Genotype VII) was performed at 28 days of age.
Summary
Newcastle disease continues to challenge poultry production operations globally causing in some countries devastating losses. Implementation of ND immunization programs must be adopted to minimize the risks involved with this viral challenge. Comparison of different ND vaccination regimens allows evaluating protection levels and consequent economic benefits. Numerous studies have demonstrated the broad spectrum of protection and lifelong immunity elicited by Vectormune® ND when compared with conventional inactivated vaccines. Maternally-derived immunity does not interfere with the immunity induced by Vectormune® ND. Additionally, it allows massive and uniform immunization when applied at the hatchery along with a live ND enterotropic strain, inducing a synergistic immune response early in the life of the bird. The superior performance of Vectormune® ND is due to its ability to avoid MDA interference and the capability to elicit all types of immunity.









