


The economic benefits of Vectormune ND vaccine on broilers at Al Ajban Farms in UAE
Introduction
Newcastle is a disease caused by a virus in the family of paramyxoviruses. It appears in three forms: lentogenic or mild, mesogenic or moderate and velogenic or very virulent, also called exotic Newcastle disease. The lentogenic strains are very widespread, but cause few disease outbreaks.1
It usually presents as a respiratory disease, but depression, nervous manifestations, or diarrhea may be the predominant clinical form.2
In low challenge countries, commercial broiler chickens are often facing the uncontrolled circulation of lentogenic (vaccine) strains, especially in high densely populated poultry areas. As a result, they may show subtle to overt respiratory signs, because of the inflammation of the trachea. As a result, flock uniformity will decrease. Ultimately, slaughterhouse condemnations may increase due to excessive airsacculitis.3
In Near East and Gulf countries, NDV circulates in waves of low to high pressure. As such vaccination against ND is considered as a routine obligation.
Ceva Animal Health introduced Vectormune ND for the active immunization of chickens against ND and Marek’s Disease. Vectormune ND is a live vector frozen vaccine that contains a genetically engineered Marek’s Disease virus of serotype 3 (HVT) expressing a key protective antigen of Newcastle disease virus that could be administered in ovo or subcutaneously in day old chicks.
The study is done to elucidate the role of Vectormune ND in protecting broilers against any ND challenge, especially Genotype VII, and providing the flock with a full immunity (cell mediated and humoral) from as early as day 21. In addition to pointing out the effect of this vaccine in enhancing the flock’s main Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in low ND challenge environment.
Materials and methods
In June 2019, 495K birds were hatched into 3 farms, Farms A and C considered as control farms and Farm B which is the trial farm. Each farm was divided into 6 floor houses and 1 cage house. 161K broilers of Farm B, trial farm, were vaccinated with Vectormune ND vaccine in the hatchery whereas Farms A and C were vaccinated with live and killed ND vaccines.
The vaccination Procedure (Vaccine Preparation and Application) was monitored by Ceva Vaccination Services (VSE) team with the assistance of Al Ajban Hatchery Manager and Megavet team.
The sampling protocol was designed by Ceva Key Account and Veterinary Services team.
Organ samples were taken from different houses of the farms at different ages, printed on FTA cards and tested by RT-PCR in Ceva accredited laboratories.
4 houses of Farm B were chosen to be tested for Vectormune ND. At least 8 spleens were taken at each sampling from each house. Sampling was done at three ages, 21 days, 24 days and slaughter age. Bursa, Trachea and Cecal tonsils samples were taken from several houses of Farms A and B to detect any IBD, ND, IBV or AIV challenge.
The flock’s KPIs were monitored in the 3 farms from hatchery till slaughterhouse, mainly the Average Bodyweight Percentage, the Processing Percentage, the Mortality Percentage, the FCR, the Dead on Arrival Percentage and the condemnation rate.
Furthermore, a descriptive analysis was done to compare the farms before, during and after the trial, and to determine if there are any statistically significant differences between the main KPIs using “The Kruskal-Wallis H test” (sometimes also called the "one-way ANOVA on ranks") and to investigate the relationship between these KPIs using the “Pearson Correlation Coefficient”.
Results and discussion
The results of the PCR tests on spleens taken from Farm B showed the prevalence of HVT-ND in almost all samples since day 21. An average of 97% of spleen samples from farm B was fully positive to Vectormune ND detection from day 21 onwards.
Both farms A and B were challenged with AIV with NO NDV nor IBDV challenge. For that, we focused not only on the immunity provided by Vectormune ND to the birds at early age, but also on the economic impact of this vaccine in NO ND challenge conditions.
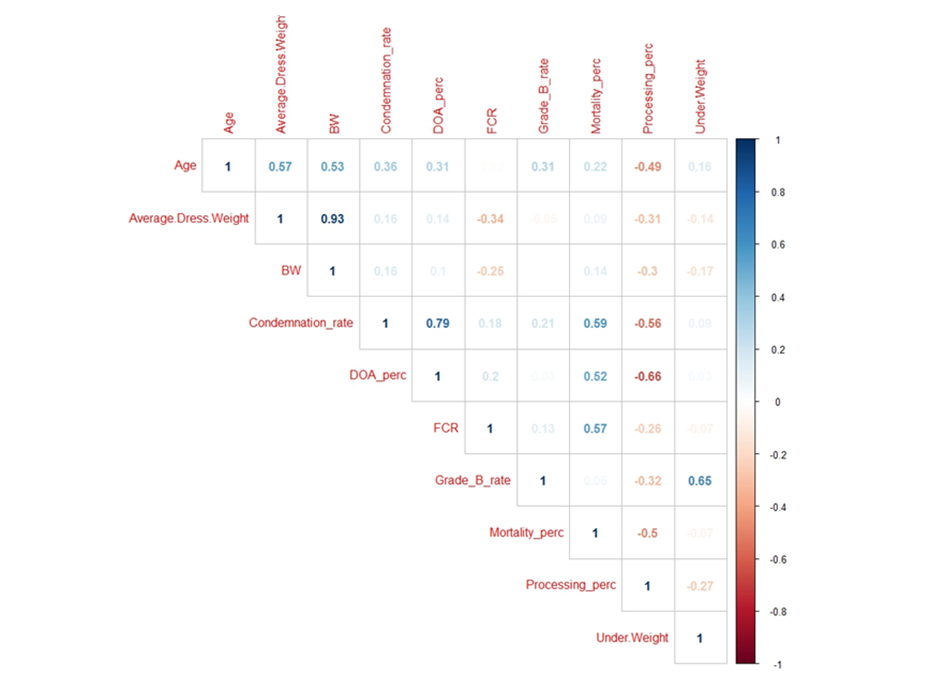
The first part of the statistical results showed a positive correlation between the FCR, the Mortality%, the Dead on arrival% and the Condemnation rate and a negative correlation with the Processing%. In other words, whenever there is a decrease in the FCR, there will be a decrease in the Mortality%, the Dead on arrival% and the Condemnation rate because they are all correlated; consequently, there will be an increase in the Processing%. (Fig1)
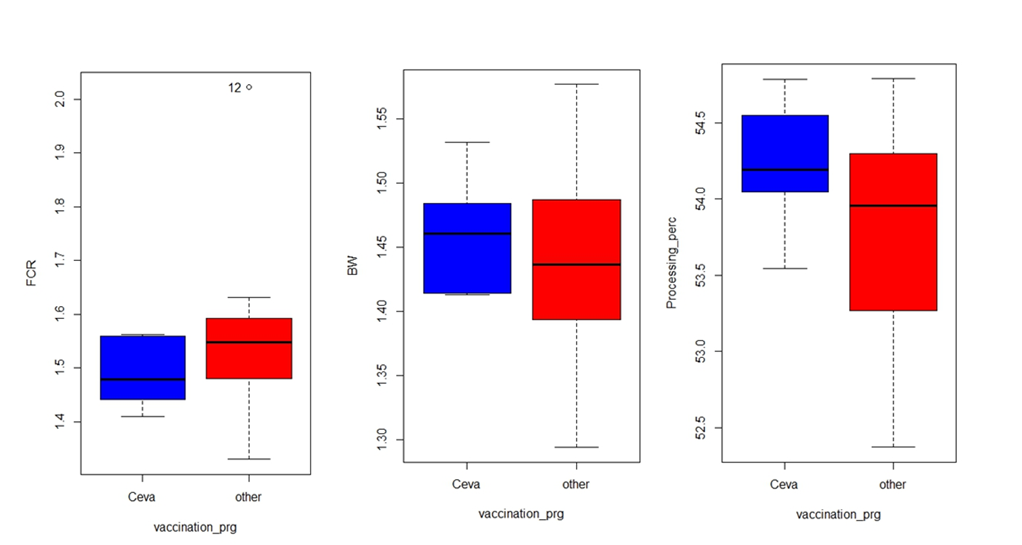
The second Part of the analysis showed the difference in FCR, Average Body weight% and Processing% between Farm B vaccinated with Vectormune ND “Ceva vaccine” and Farms A&C (others) vaccinated with conventional ND vaccines during June (The month of the trial), before and after the trial.
Even though the health situation of all farms was remarkably good during this month, Farm B was heading the other farms in performance; i.e. FCR of farm B was lower than the others (and consequently the condemnation rate, the Mortality% and the Dead on arrival%).
In addition, the ABW% and the Processing % of Farm B are higher and more homogenous than others. (Fig. 2)
The following figures (Fig.3,4&5) showed the difference between the farms, before (April, May) during (June) and after the trial (August).
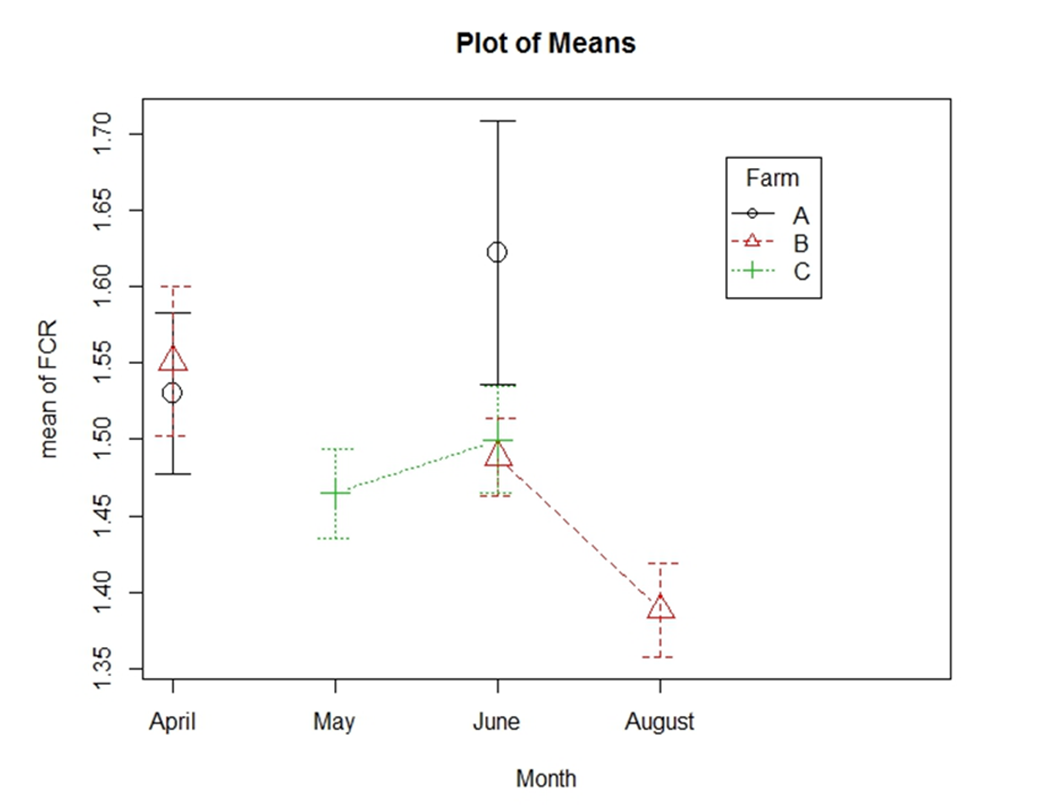
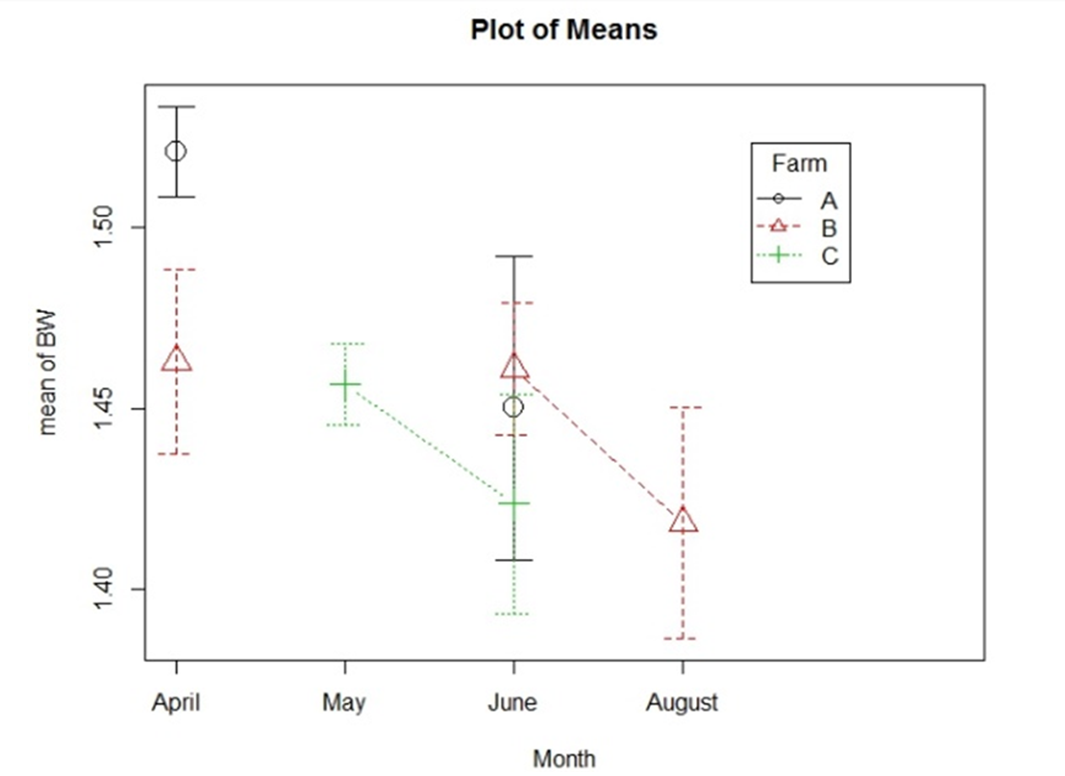
The condition of all farms was getting better from May till August. However, during the trial month ‘June’ Farm B was even better than the two other farms in FCR, ABW% and slightly in the condemnation rate.
Conclusion
Considering the pathogenicity of NewCastle Disease virus and its economically and clinically importance worldwide, Ceva installed the ultimate antivirus “Vectormune ND” which provides maximum protection to the birds with no side effects and reduces the virus shedding effect. Moreover, in low challenge ND environment, Vectormune ND positively impacts the performance of the birds through the amelioration of the FCR, the Average Bodyweight Percentage and consequently the Production Index generating more income to the Farmer.
| References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 https://www.vectormune.com/Newcastle-Disease/Why-is-ND-still-a-threat-to-the-poultry-industry | ||||
| 2 https://www.oie.int/en/animal-health-in-the-world/animal-diseases/Newcastle-disease/ | ||||
| 3 https://www.vectormune.com/Newcastle-Disease/What-is-Newcastle-disease-ND | ||||












