


Caecal Worm
Introduction
Heterakis gallinae, nematode parasites of poultry and game birds, are small whitish worms with a pointed tail, up to 1.5 cm in length that occur in the caecum. They are found worldwide. Morbidity is high but it is not associated with mortality. Infection is by the oral route. Earthworms may be transport hosts for eggs, or paratenic hosts with partially developed (L2) larvae. There is an incubation period of 2 weeks for eggs to embryonate, and a four-week prepatent period. The meaning of the technical terms relating to parasite life cycle are defined in the glossary. Heterakis gallinae eggs and larvae are a transport hosts for Histomonas, the cause of Blackhead.
Signs
- None.
Post-mortem lesions
- Inflammation of caecum, possibly with nodule formation.
Diagnosis
Adults can be seen in caecal contents at post-mortem examination.
Treatment
Flubendazole, Levamisole, are effective.
Prevention
Avoiding access to earth and earthworms. Routine anthelmintic treatment.
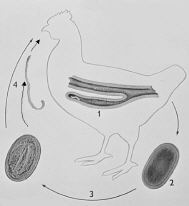 |
| Figure 11. The life cycle of Heterakis showing the location of adults, an undeveloped egg as found in fresh faeces, and the embryonated egg. The egg may be ingested directly by a chicken, or by an earthworm which is in turn ingested by a chicken. |
Extracted From:
A Pocket Guide to Poultry Health and Disease by Paul McMullin© 2004







