
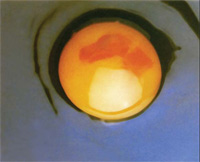
Blood spots
Description
Blood spots vary from barely distinguishable spots on the surface of the yolk to heavy blood contamination throughout the yolk. Occasionally blood may be diffused through the albumen or white of the egg.
Incidence
The incidence varies between strains of bird and can be as high as 10%. Between 2 and 4% of all eggs contain some blood.
| Cause | Control |
|---|---|
| Blood vessels rupturing in the ovary or oviduct, affected by: | |
| Levels of vitamin A and vitamin K in the die | Keep vitamin premixes cool and dry. If you prepare your own, they must be properly formulated and mixed. |
| Vitamin K antagonists (e.g. the drug sulphaquinoxaline and a component of lucerne meal) | Layer diets should not contain high levels of lucerne meal. Withdraw the drug sulphaquinoxaline from layers at least 10 days before collecting eggs for human consumption and follow any other requirements for correct medication. |
| Fungal toxins | Do not allow feed bins or feed lines to become contaminated by stale, wet or mouldy feed. |
| Lighting programme | Do not use continuous light, or light programmes consisting of short, intermittent light periods. |
| Frights and disturbances | Take care that birds are not disturbed by unusual or sudden loud sounds in the layer shed. |
| Avian encephalomyelitis | Follow an effective vaccination programme. |
| Strain of bird | Incidence of this fault may be higher in some strains. |
COPYRIGHT NOTICE: OPTIMUM EGG QUALITY - A PRACTICAL APPROACH
© The State of Queensland, Australia (through its Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries) and DSM Nutritional Products Ltd., 2007. No part of this publication may be reproduced, copied or transmitted save with prior written permission of Director, Intellectual Property Commercialisation Unit, Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, GPO Box 46 Brisbane, Queensland, Australia 4001, and DSM Nutritional Products Ltd.
© The State of Queensland, Australia (through its Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries) and DSM Nutritional Products Ltd., 2007. No part of this publication may be reproduced, copied or transmitted save with prior written permission of Director, Intellectual Property Commercialisation Unit, Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, GPO Box 46 Brisbane, Queensland, Australia 4001, and DSM Nutritional Products Ltd.






