|
Histopathology and Cytology of
Poultry Diseases By Ivan Dinev, DVM, PhD
|
STAPHILOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS
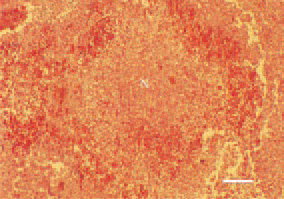
Fig. 1. Widespread coagulative necrosis (N) in the liver, surrounded by a haemorrhagic zone as a manifestation of staphylococcal septicaemia in a hen. H/E, Bar = 35 µm.
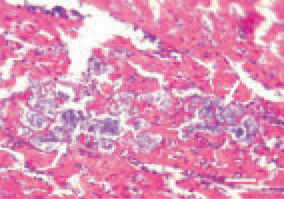
Fig. 2. Interstitial and parenchymatous myocarditis in a broiler chicken. Bacterial colonization and bacterial thrombi in the myocardium (arrows) in staphylococcal septicaemia. H/E, Bar = 25 µm.
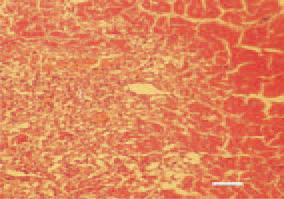
Fig. 3. Myocardial infarction (I) in a bird that has survived a staphylococcal septicaemia. H/E, Bar = 30 µm.
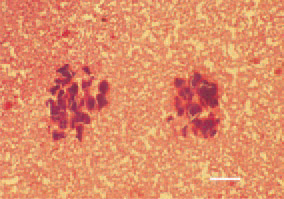
Fig. 4. Bacterial emboli obturating capillary sinusoids and intensive degenerative necrobiotic lesions of the liver, resulting from metastasis of a local focus of staphylococcal infection. H/E, Bar = 35 µm.
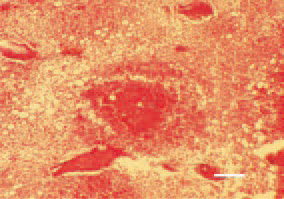
Fig. 5. Staphylococcal osteomyelitis, secondary to septicaemia. An inflammatory necrotic focus, bacterial colonization and bone marrow congestion. H/E, Bar = 30 µm.
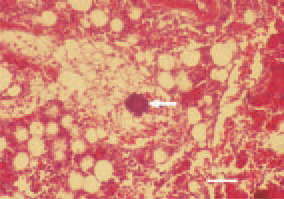
Fig. 6. Staphylococcal osteomyelitis. Bacterial thrombus (arrow) obturating a bone marrow sinusoid. H/E, Bar = 25 µm.
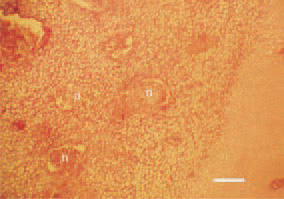
Fig. 7. Staphylococcal osteomyelitis. Focal inflammatory necrotic lesions in the growth plate of the proximal femur in a broiler chicken. H/E, Bar = 40 µm.
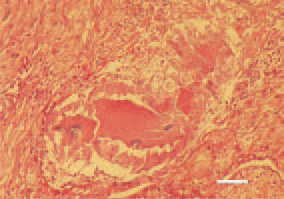
Fig. 8. Staphylococcal tenosynovitis. Serofibrinous exudate filling the synovial space, central necroses, with clusters of bacterial colonies among them. H/E, Bar = 25 µm.
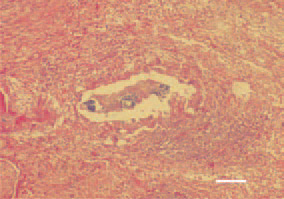
Fig. 9. Staphylococcal tenosynovitis. Central caseous necrotic lesions and clusters of bacterial colonies. Intensive inflammatory cell reaction (lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages) affecting the tendon sheath layers. H/E, Bar = 40 µm.
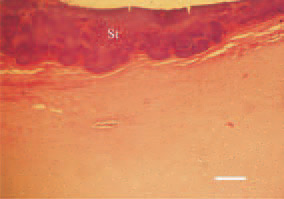
Fig. 10. Staphylococcal arthritis. Degenerative necrobiotic lesions and massive bacterial colonization (St) of the distal femoral articular cartilage in a growing male broiler breeder. H/E, Bar = 40 µm.
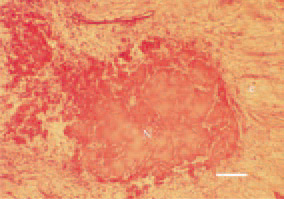
Fig. 11. Staphylococcal tenosynovitis. Axial necrosis (N) of a tendon and perifocal inflammatory oedema (e). H/E, Bar = 30 µm.






