|
Histopathology and Cytology of
Poultry Diseases By Ivan Dinev, DVM, PhD
|
CHOLANGIOHEPATITIS
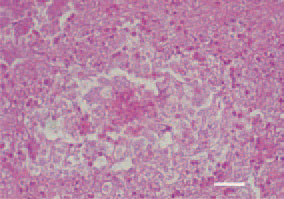
Fig 1. Liver. Multiple outgrown bile ducts, forming a granuloma structure with a central necrosis. H/E, Bar = 35 µm.
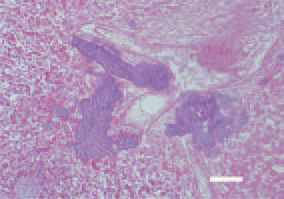
Fig. 2. Liver. A biliary stasis and a huge amount of Gram-positive organisms in bile ducts. Gram staining, Bar = 25 µm.
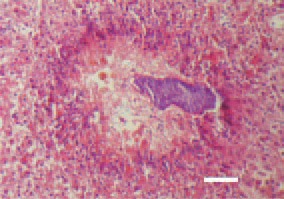
Fig. 3. Liver. Pericanalicular biliary necroses. H/E, Bar = 50 µm.
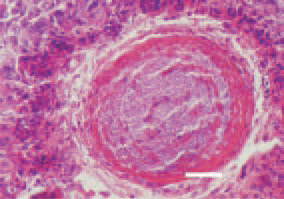
Fig. 4. Liver. Fibrosed and thickened wall of a bile duct, filled with Grampositive microorganisms after the occurred inflammatory and necrotic changes. H/E, Bar = 35 µm.
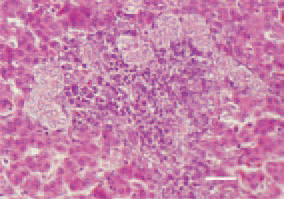
Fig. 5. Hepatosis in the liver of a broiler chicken. Proliferation of bile ducts and fibrous tissue, that have infiltrated the portal zones through mononuclear cells. H/E, Bar = 25 µm.
This book is protected by the copyright law.
The reproduction, imitation or distribution of the book in whole or in part, in any format (electronic, photocopies etc.) without the prior consent, in writing, of copyright holders is strictly prohibited.






