|
Histopathology and Cytology of
Poultry Diseases By Ivan Dinev, DVM, PhD
|
VIRAL ENTERITIS COMPLEX (RUNTING STUNTING SYNDROME)
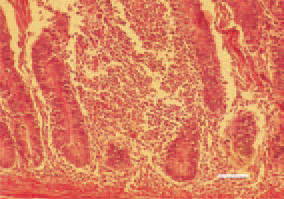
Fig. 1. Diffuse inflammatory cell proliferate in small intestinal mucous coat. Chickens at the age of 5 - 12 days are affected. Etiologically, reoviruses, astroviruses and rotaviruses, individually or collectively, are involved. The possible vector of infection are the larvae of the lesser mealworm beetle Alphitobius diaperinus. H/E, Bar = 100 µm.
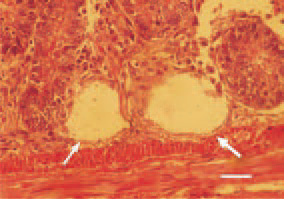
Fig. 2. Appearance of cystic crypts (arrows) in duodenal mucosa. The primary cause is possibly a retention resulting from the compression of the inflammatory proliferate in the mucous coat. H/E, Bar = 35 µm.
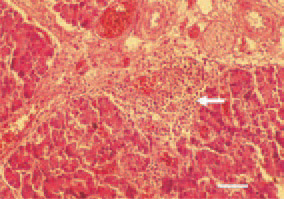
Fig. 3. Perivascular inflammatory cell proliferate in the pancreas (arrow). H/E, Bar = 50 µm.
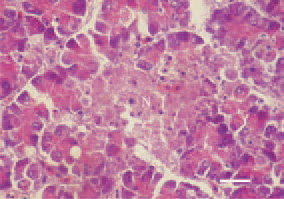
Fig. 4. Focal necrosis (N) in the pancreatic parenchyma. H/E, Bar = 25 µm.
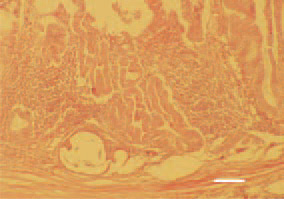
Fig. 5. Inflammatory proliferative and cystic lesions in the mucous coat of the proventriculus. H/E, Bar = 100 µm.
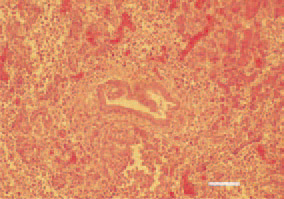
Fig. 6. Hyperplasia of pancreatic ducts and mononuclear cell infiltration in the portal zone. H/E, Bar = 50 µm.






